What’s the Best Pipe for Underground Water Supply?
One of the most prevalent — and important — uses of piping in our construction and infrastructure is for water supply, an application that requires a piping material that can perform in hot and cold temperatures, resists corrosion and leaking, and is free of harmful chemicals. For underground water supply lines, add to these requirements the ability to hold up in a variety of soil and environmental conditions and to be installed in a method suitable to the location.
Types of Underground Water Supply Pipes
The right type of pipe for underground water transport is dependent on factors such as the installation location, local regulations, and more—the answer is extremely context-dependent and should be based on the requirements of the specific application.
Below, we run through some of the most common underground water pipe materials and their performance characteristics, drawbacks, and benefits for water supply uses.
1. Copper
Copper piping has been used in plumbing and water supply applications for years because it resists corrosion and protects water quality. Copper pipes can withstand high temperatures and water pressures, as well as be recycled. However, copper is extremely rigid, as well as higher priced than other water supply piping options, making it unsuitable for some applications.
2. Cast Iron
Cast iron piping is still in use in many water transport systems, but it’s generally a legacy part of the system and is rarely used in new construction. Despite the heat resistance and noise-dampening properties of cast iron, it’s not as suitable for underground water supply as newer materials. Cast iron is not resistant to corrosion, which can compromise the quality of the water supply and damage the integrity of the piping, leading to leaks and breaks.
3. Galvanized Steel / Lead
Like cast iron, galvanized steel and lead pipe have been used historically for water transport. These materials are problematic for use with water due to their susceptibility to corrosion. When these types of pipes corrode, hazardous materials can enter the water supply and cause severe threats to human health, as made evident by the Flint water crisis.
4. PVC
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is one of the most common types of piping, and it can be used for underground water supply in some applications. PVC is generally inexpensive and is a reliable, durable material. It is rigid, resists corrosion, and can have a lifespan of over 100 years.
PVC piping is joined via either threaded fittings or solvent welding (a gluing process). Fusible PVC® is a newcomer to the market and is joined through a specialized thermal butt fusion process, similar to that used for HDPE pipe.
The use of PVC for underground transport of potable water is restricted in some areas, due to concerns about the potential for chemicals to leach into the water. The material currently meets the American Water Works Association (AWWA) requirements for use with potable water, but certain states relegate its use to non-potable applications, such as underground irrigation.
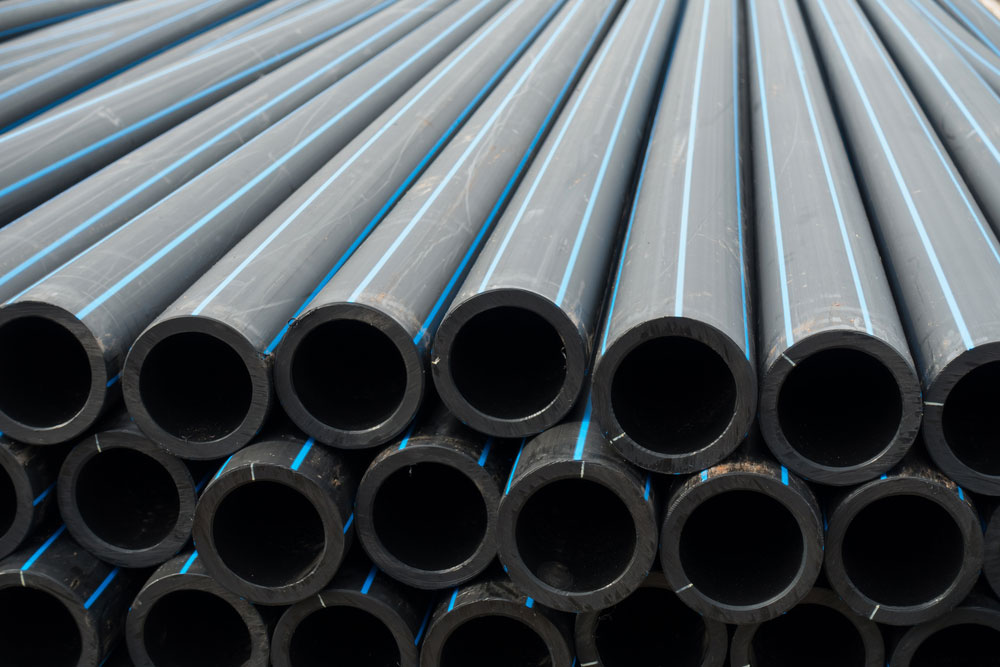
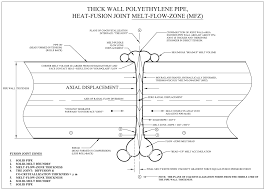
5. HDPE
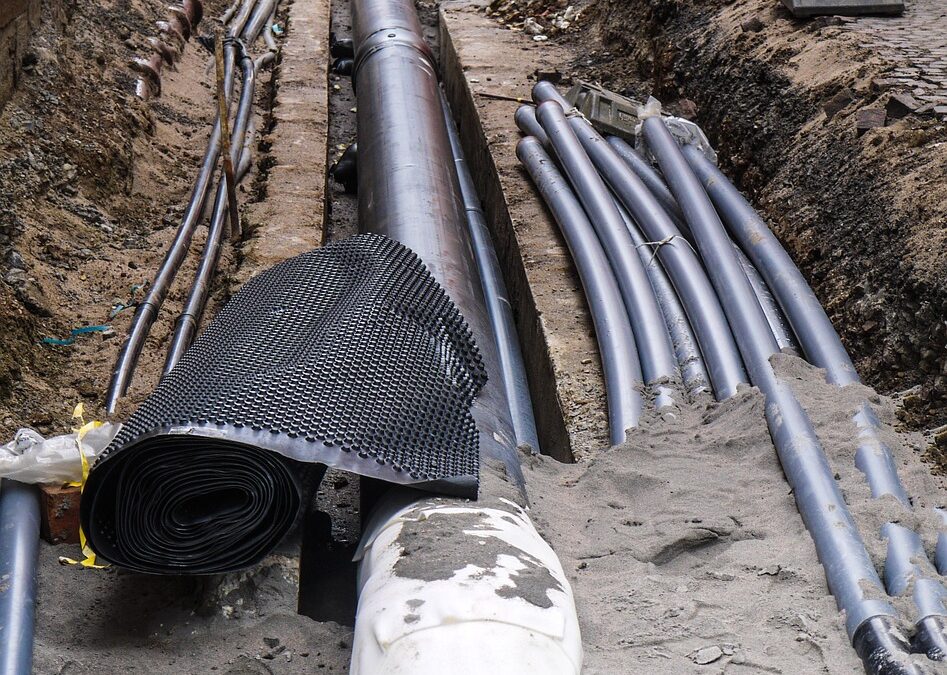
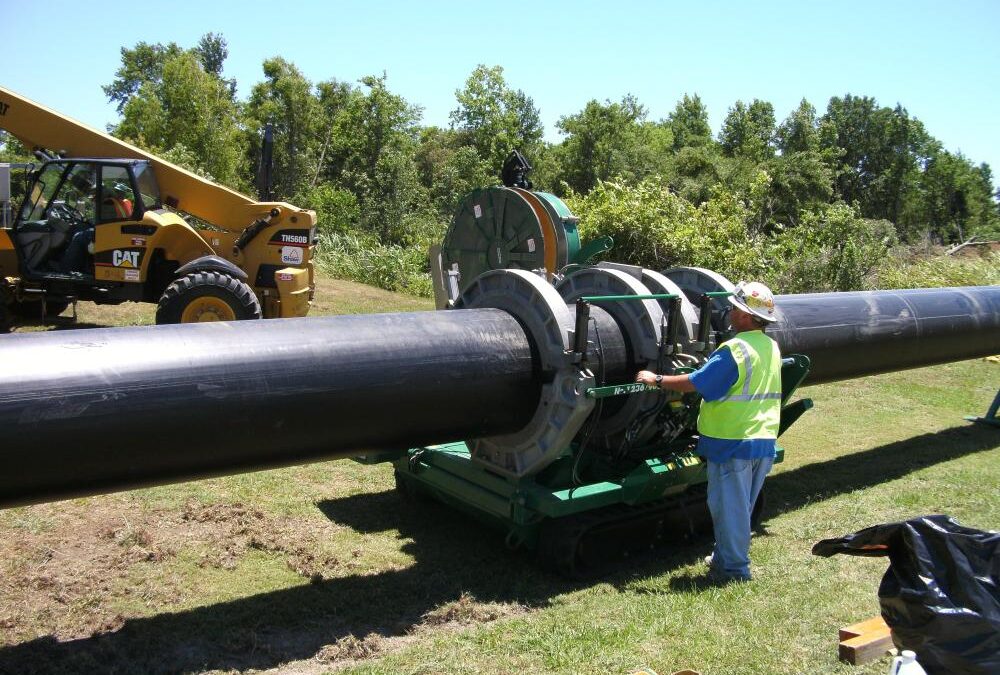
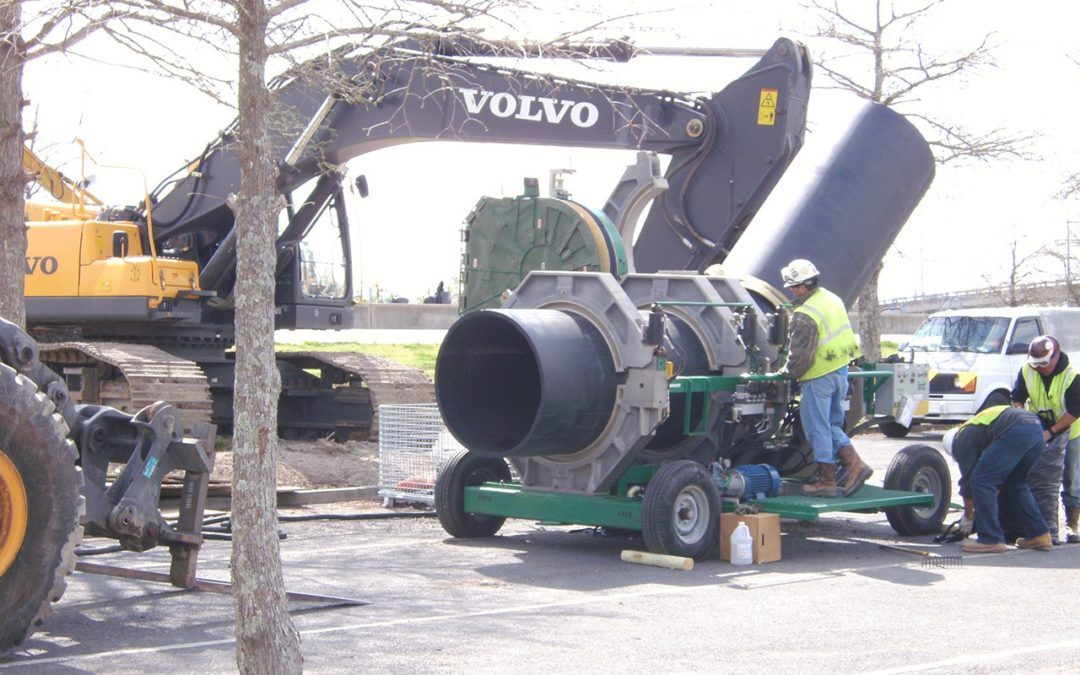
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipe is a good choice for underground water lines because of how the pipe is connected. Rather than using joints, which can leak, or glues and cement, which can degrade over time, HDPE pipe is connected via plastic fusion. In thermal butt fusion, a common fusion method, the pipe is aligned end to end and then high heat is applied, melting the pipes together seamlessly. HDPE is extremely durable, with a lifespan of upwards of 100 years.
Like other non-metal pipe materials, it is resistant to corrosion; unlike other materials, HDPE is flexible. This is beneficial as it can increase resistance to shifting soils due to environmental conditions or even events such as earthquakes. This flexibility also allows for trenchless installation methods.
HDPE can be installed using any of a variety of methods, not just drop burial or open trench installation. This makes it more versatile than most other pipe materials suitable for underground water supply. HDPE piping can be installed via sliplining or horizontal directional drilling, which may in some cases be the best, most cost-effective installation method.
Contact the HDPE Pipe Specialists at US FUSION
For your underground water supply needs, contact US Fusion. Our HDPE pipe offerings are suitable for underground water transport, offering leak-free performance, corrosion resistance, and a long lifespan. We’re able to install HDPE pipe using a variety of fusion techniques, including butt fusion, saddle fusion, socket fusion, and electrofusion, and can employ trenchless and trench installation methods.